你可能感兴趣的试题
剧烈运动:当b+c>b'时 急性肠炎:当b+c>b' 发高烧:当b+c=b'时 正常状态:当b+c=b'时
1000ml 2000ml 500ml 1500ml 2500ml
剧烈运动:当b+c>b″ 急性肠炎:当b+c>b″时 发高烧:当b+c=b″时 正常状态:当b+c=b″时
1400~1500ml 1000~1200ml 140~150ml 70~75ml 45~50ml
1000ml 1500ml 2000ml 2500ml 300ml
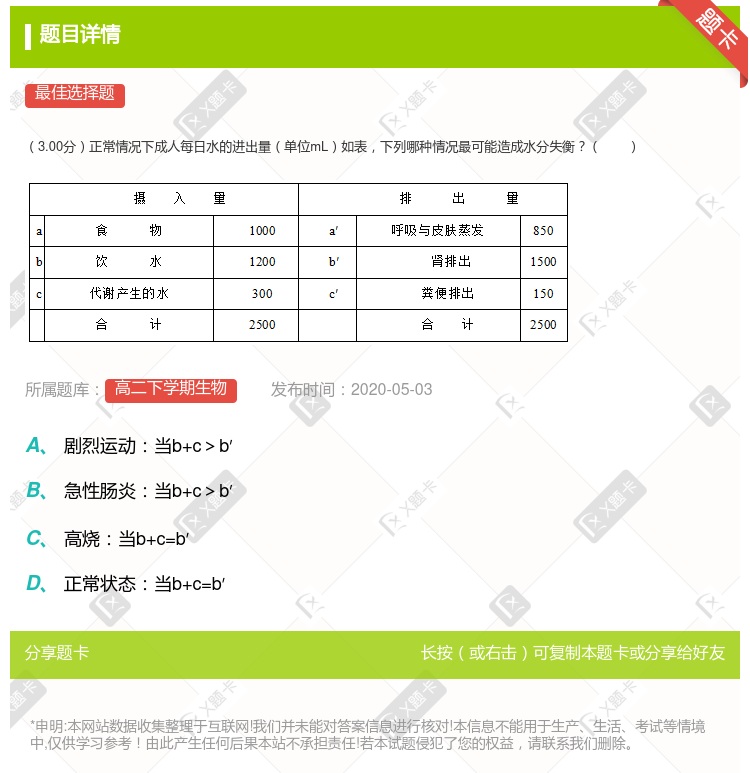
呼吸及皮肤蒸发:850| b饮水:1200 | 肾排泄:1500 |
| c代谢产生的水:300 | 粪便排出:1500 |
| 合计:2500 | 合计:2500 |
上表为正常情况下,成人每日水的进出量(mL)依据上表数据,分析下列哪种情况最可能造成水分进出的失衡: A.剧烈运动:当b+c>B 时 B.急性肠炎:当b+c>B时 C.发高烧:b+c=B 时 正常状态:当b+c=B时
1000ml 1500ml 2000ml 2500ml
正常情况下每次尿量为 200-400ML 正常情况下 24小时尿量为 1000-1500ML 正常情况下 24小时尿量平均为 1200ML 正常情况下每次尿量为 300-500ML 正常情况下 24小时尿量为 500-1000ML
剧烈运动,当b+c> b1时 急性肠炎,当b+c> b1时 发高烧,b+c= b1时 正常状态,当b+c= b1时